Description
We Other Utopians is the first book to explore recombinant DNA/genome editing issues based on ethnographic research in the post-communist context. The book focuses on the topics of human DNA editing and genome repair at two levels. First, inspired by texts that analyze the concept of life and the body in general, it works conceptually and analytically with various approaches to designed life and incarnations from the perspective of anthropology, sociology, and science and technology studies.
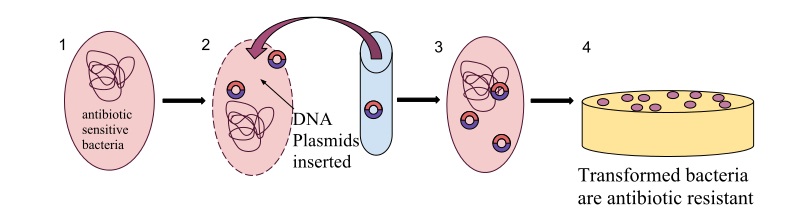
Second, it presents an analysis of artificial life and biotechnological achievements in specific technologies: genome editing, other recombinant DNA and biological computing. The book explores the topic of genome editing based on ethnographic research carried out in a biochemical laboratory in the Czech Republic. The fieldwork was carried out between 2017 and 2019, mainly in a laboratory focused on DNA damage and genomic risk of complex diseases or genetic vulnerabilities such as breast cancer, infertility and aging.
Recombinant DNA is understood here as the exchange of DNA strands to produce and design new arrangements of nucleotide sequences to cure or improve human bodies and health in the future. The book examines various economies of hope, hype, expectations, the politics and poetics of false promises and better or worse predictions from the standpoint of sociology, anthropology, and science and technology studies.
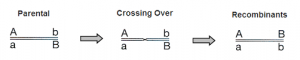
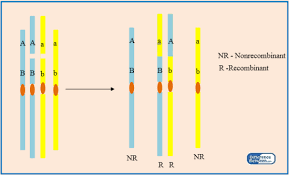
Linked gene recombinants are those combinations of genes that are not found in the parents.
- Recombinants are produced as a result of crossing over of genetic material during prophase I of meiosis.
- If linked genes are separated by a chiasm, there will be an allele exchange between non-sister chromatids.
- This creates new combinations of alleles that are different from the parent.
The frequency of recombinant phenotypes within a population will normally be less than that of non-recombinant phenotypes.
- This is because crossing over is a random process and chiasmata do not form in the same places with each meiotic division.
The relative frequency of recombinant phenotypes will depend on the distance between linked genes.
- The frequency of recombination between two linked genes will be higher when the genes are further apart on the chromosome.
- This is because there are more possible locations where a chiasm could form between genes.